Necessity of Self-Regulatory Operations
The trading of various financial instruments, such as equities (e.g., stocks) and derivatives (e.g., stock index futures), is conducted on Japan Exchange Group's subsidiaries Tokyo Stock Exchange and Osaka Exchange. This section explains the necessity of self-regulatory operations in the roles of the exchange.
The Roles of the Exchange
Price Discovery
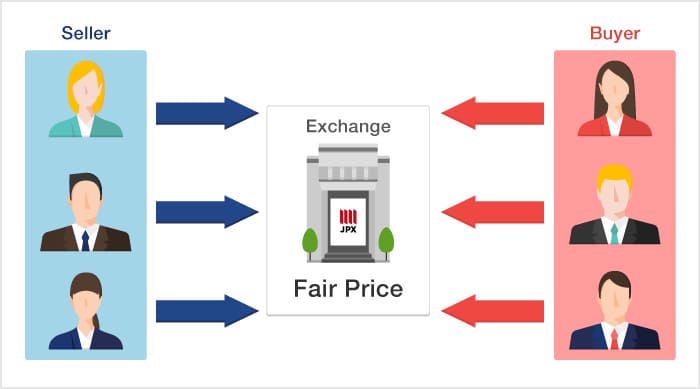
In order for a stock trade to be executed, there must be both a buyer and a seller. Its price is also an important factor.
The exchange collects the buy and sell orders for a stock, conducts an auction to determine the stock's price, and executes the trade.
Providing a Venue for Raising Funds
Providing a venue for companies to raise funds is another important role of the exchange. It is to their advantage to list their shares on the exchange.
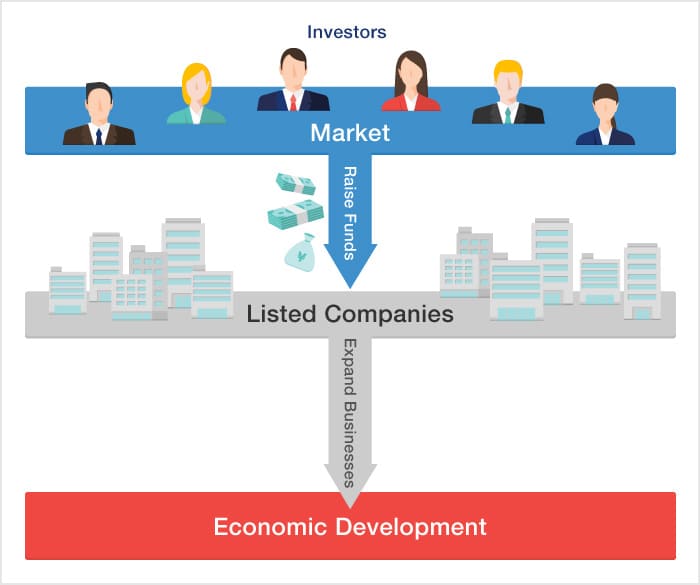
In addition to borrowing from banks and other financial institutions, a company can raise the funds necessary for its business operations by issuing new shares. If it lists those shares on the exchange, their price may fluctuate, but investors are more likely to buy them because they can easily sell them back for cash and recover their investment. The exchange makes it easier for companies to raise funds through issuing new shares, which helps them expand their businesses.
By providing a venue for share trading, the exchange makes an excellent environment for companies to issue shares and raise funds. Companies can use those funds to expand their businesses, and this contributes to the development of the economy as a whole.
The Importance of the Exchange's Self-Regulatory Operations
Rules for Fulfilling the Exchange's Roles and Market Players
In order to smoothly and stably fulfill its roles and mission, the exchange will establish various rules and mechanisms on top of the government's laws and regulations.
This includes not only establishing rules for determining the prices for executing trades but also limiting those who can place orders on the exchange to qualified securities companies (trading participants) and setting the criteria for listing stocks.
The exchange will grant trading participant qualifications to securities companies that have established systems to fully understand and comply with the government's laws and the exchange's rules. By enforcing the rules on these qualified securities companies (trading participants), the exchange establishes a mechanism to facilitate the smooth and stable execution of orders from many investors.
In addition, since a company is the source of the value of its listed stock, the exchange will establish listing criteria, and only the stocks of companies that are deemed to meet such criteria will be listed (companies that issue listed stocks are called listed companies). The exchange will also establish delisting criteria, and if a listed company is deemed to be no longer suitable for investment and satisfies the delisting criteria, its stock will be delisted.
In this way, the exchange fulfills its roles and mission by winning the trust of investors who believe that it is operated in accordance with the rules that it has established.
To Prevent Damaging Investors' Trust in the Exchange
On the other hand, if the following situations are left unaddressed, investors may suffer unforeseen losses and lose confidence in investing.
- Trading participants violate the rules
- Malicious investors engage in fraudulent transactions
- There are newly listed companies that do not meet the listing criteria
- Companies make disclosures containing false information or omitting information that investors consider most important when making investment decisions
If the exchange loses the trust of investors, it will be unable to fulfill its roles and mission. This may ultimately have a negative impact on economic development.
To prevent such situations from occurring, it is extremely important for the exchange to perform quality control when fulfilling its roles and mission. The exchange's self-regulatory operations serve as such quality control.
The environment around the exchange, as well as the circumstances of its trading participants and listed companies, are constantly changing. By continually monitoring such changes and promptly addressing any issues that could lead to unforeseen circumstances for investors, the exchange can maintain and improve its fairness and reliability.
This is why the exchange's self-regulatory operations are so indispensable.



