Risks (ETNs)
Futures-Type ETNs
Futures-Type ETNs refer to ETNs tracking indicators that use prices of futures contracts or those to conduct investment in mainly futures contracts.
A Closer Look at Futures-Type ETN Investment
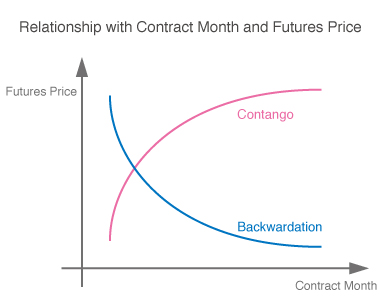
Futures prices vary depending on contract months (settlement cycle for futures) (*). The reason is time value. The time value shows expectation for price movements during the period from the present to a contract month. Storage costs, etc. (cost of carry) are also reflected in the price for commodity futures.
In general, because the further away you are from the contract month, the more uncertain the future prices will be, the time value becomes larger and futures prices become higher. Situations where the futures price is higher in a deferred contract are called contango; whereas, situations where the futures price is lower in a deferred contract (meaning that prices in the near-term contract are higher than those in the deferred contract) are called backwardation.
Such factors may lead to gains and losses in futures-type ETNs that are associated with the underlying indicator due to the transfer of positions in a contract month to a subsequent contract month (rollover).
Particularly, commodities futures or volatility index futures, including Nikkei 225 VI Futures, tend to veer toward contango. Futures-type ETNs that use such futures prices may reduce in price due to repeated rollover associated with the underlying indicator. Thus, mid- and long-term investment warrants attention.
- Options contracts and futures contracts expire on a certain month. The expiration month is called a contract month.
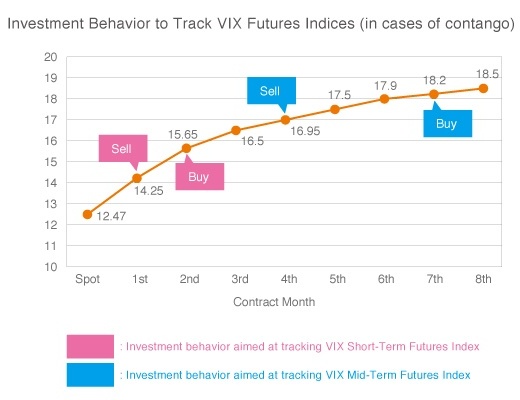
Let's look at the price of each contract month of VIX Index futures as of December 3, 2014. You will find that contango occurs where a futures price can be higher in the deferred contract. Assume that there are no changes in the futures price.
Typical VIX futures indices are calculated by indexation of earnings ratio where the first month futures contracts are sold; the second month futures contracts are purchased on a regular basis; and, the remaining days are maintained for a certain period. This means that repeated rollovers where low-priced near-term futures contracts are sold (ex., the second month futures contract is sold at USD 14.25) and high-priced deferred futures contracts are purchased (ex., the second month futures contract is purchased at USD 15.65) occur. In this situation, VIX futures indices will constantly reduce in price against the relevant VIX index. The impact of time value of futures tends to become greater than that of contract months in near-term contracts. Thus, the reduction of futures indices pegged to time value tends to be larger in the VIX Short-Term Futures Index managed in near-term contracts than that of the VIX Mid-Term Futures Index managed in deferred contracts.
ETNs tracking indicators that use prices of commodity futures and volatility index futures
The table below presents Futures-type ETNs listed on the TSE market. The characteristics of each ETN are disclosed in the securities registration statements of the ETNs and on the websites of issuers. Pay close attention to such information when investing in ETNs.
Commodity Futures
NEXT NOTES Gold Futures Double Bull ETN (2036, Nomura Europe Finance N.V.) *In Japanese only
NEXT NOTES Gold Futures Bear ETN (2037, Nomura Europe Finance N.V.) *In Japanese only
NEXT NOTES Dubai Crude Oil Futures Double Bull ETN (2038, Nomura Europe Finance N.V.) *In Japanese only
NEXT NOTES Dubai Crude Oil Futures Bear ETN (2039, Nomura Europe Finance N.V.) *In Japanese only



